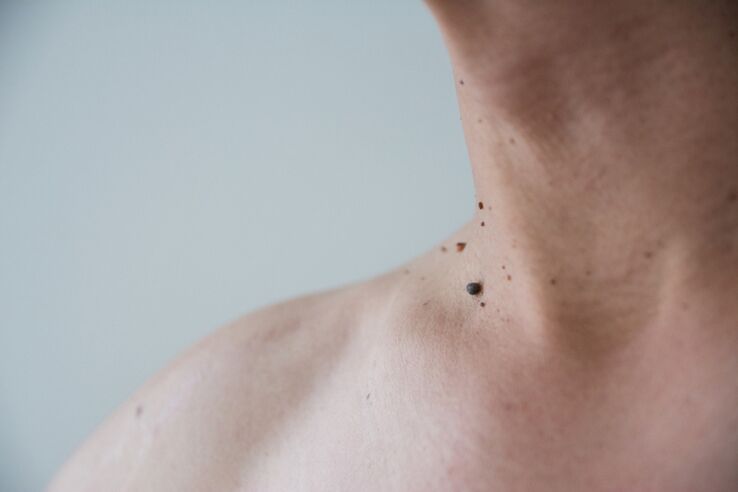
There are very few people who do not have a problem like warts on the body. These growths can occur in adolescents, adults and the elderly. Warts usually worsen a person's appearance and become a cosmetic problem. And only in rare cases do these formations pose a real threat to health.
What is a wart?
Our skin is smooth. However, in some cases, overgrown skin may appear on it. They are called warts. Typically, these are stable formations that have not changed over the years.
The mechanism of wart formation is the growth of the top layer of skin. Formations range in size from 1 mm to several centimeters. This setting depends on the type of makeup and its location on the skin. Several warts merge. The color of the skin growth is mostly fleshy, but they can take on other shades, such as pink or brown.
Medicine classifies warts as benign tumors. They do not grow and do not penetrate the surrounding tissues.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, warts have the following codes:
- B07 - viral warts,
- A63. 0 - venereal wart,
- L82 Seborrheic keratoma
Most types of warts are viral, sexually transmitted bones are venereal, and seborrheic keratomas are non-infectious old warts.
The following skin lesions should be distinguished from warts:
- nevi (mole),
- callus,
- malignant tumors,
- basal cell carcinoma,
- broad warts caused by syphilis.
Some of these formations can be life threatening. Therefore, if there is any suspicion in the body, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Why do warts form?
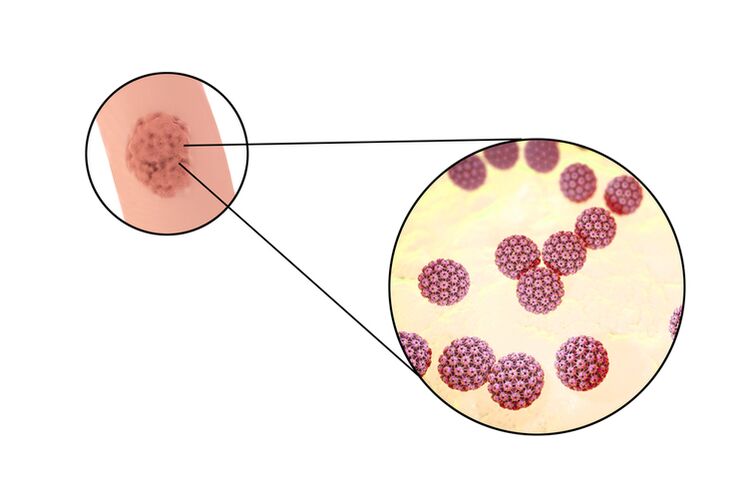
A viral infection usually causes warts. The process of wart formation is as follows. Human papillomavirus enters the skin cells and causes them to divide rapidly. As a result, growths or papillomas appear on the skin. However, there are types of warts that have nothing to do with the virus.
In particular, papillomas do not always occur on the skin. Most often, these structures are found in the mucous membranes, inside the bladder, larynx, cervix, etc. b. However, it has become customary to call warts only skin papillomas.
Warts can be located anywhere on the body. However, some species have favorite places. For example, warts usually appear on the groin and in the groin; Acrochords like the folds of skin on the upper part of the body.
Human papillomavirus does not multiply outside the body. However, it can be stored for a long time in warm and humid places. Therefore, people can become infected when they go to baths, saunas and swimming pools. However, the virus does not live long in the open air - it is neutralized by the sun's ultraviolet rays.
According to research, about 80% of the world's population is infected with some form of human papillomavirus. In all, there are two hundred strains of the virus. Some viruses are relatively harmless, others cause papillomas, and others can cause malignant tumors. Some strains can be transmitted from person to person. Therefore, some types of warts can be contagious. However, the disease cannot be transmitted from frogs and toads, as well as other members of the fauna, against popular belief. This is because the papillomaviruses of these animals do not multiply in the human body.
The new type of virus can be transmitted through personal contact, handshakes, sharing household items (such as towels), visiting public places (swimming pools, baths, saunas, vehicles), minor injuries, and sexual contact.
Absorbed papillomavirus does not always cause the disease. Usually, the factors associated with this disease are stress, decreased immunity (for example, due to infectious diseases). At the same time, the virus can remain in the body for several years and wait in the wings.
Types of warts
Doctors distinguish several types of warts:
- normal
- young (flat),
- condylomata
- old age,
- threadlike.
Birthmarks (nevi) should be distinguished from these types of warts. Birthmarks usually do not appear on the skin and are black, regardless of color.
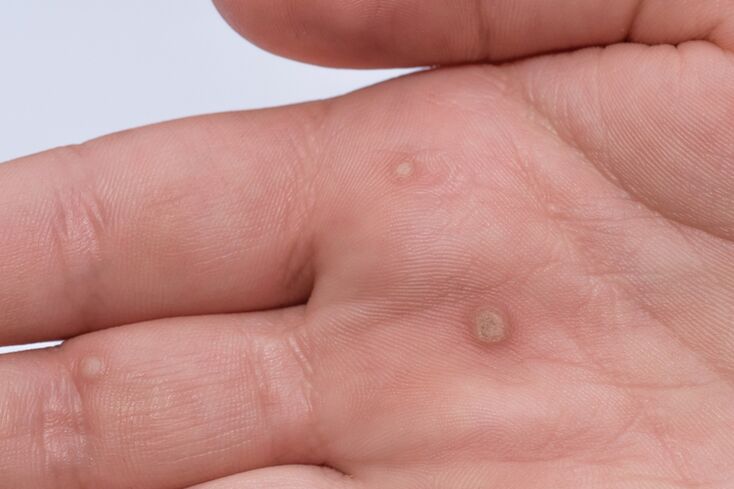
Vulgar warts
This type of wart is found in 70% of cases. It is caused by the papilloma virus. In appearance, vulgar (normal) papillomas resemble small semi-circular formations on the surface of the skin. They usually do not hurt at all. The formations range in size from a few millimeters to 1 cm, and their surface is usually uneven, convex, often resembling the surface of a colored cabbage. Color - flesh-like, pale yellow-brown. Multiple localization - hands, face, fingers, lips, knees, elbows. The mucous membranes are rarely damaged.
Normal papillomas can usually go away on their own. The peculiarity of this type of papillomas is that they often grow in groups, not alone. Large papillomas are more common, with smaller ones growing around them. If you remove the largest (ovarian) papilloma, the smaller ones will usually disappear.
Normal papillomas can occur at any age. They are most common in school-age children.
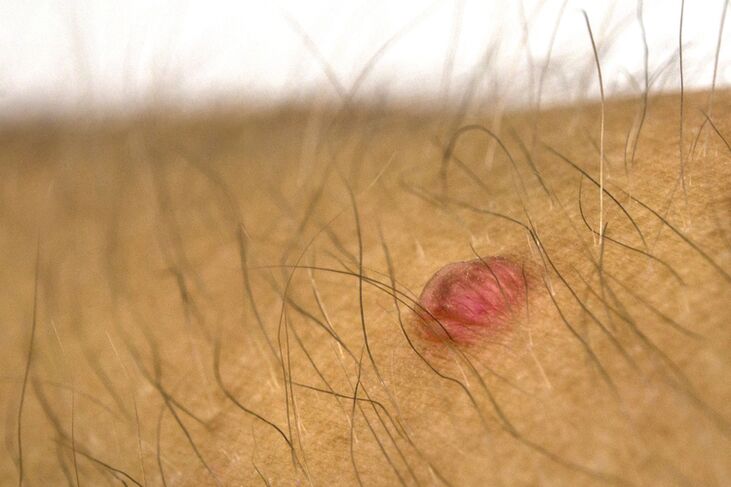
Adolescent warts
This type of papilloma is more common in children and adolescents. However, they can occur in adults. These papillomas are often called flat papillomas. They make up only 4% of the warts.
You can often find them on hand. They can also be seen on the feet and face, near the nails, between the toes, on the feet and neck. They are often due to hormonal changes in the body. Like normal papillomas, they do not pose a serious risk and can go away on their own. They usually do not cause physical discomfort, but can worsen their appearance.
Flat papillomas are usually fleshy and protrude slightly above the skin surface (approximately 1-2 mm). They can be up to 5 mm in diameter, but are usually smaller than vulgar. Flattened papillomas can appear near sores and wounds. Usually, the surface of juvenile papillomas is smooth and uneven, although the boundaries are clearly defined. Since there is no outer layer, they may look shiny.
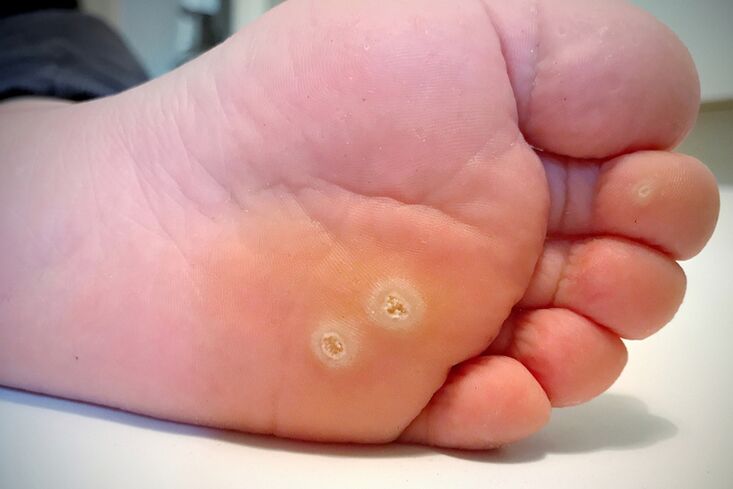
Plantar warts
This is a very unpleasant form of skin growth that occurs on the feet. Sometimes they are mistaken for corn. However, plant papillomas have a feature that distinguishes them from corn. If a wart is injured, it usually bleeds. This is not the case with corn. In appearance, papillomas on the legs may look like calluses - they are usually hard and keratinized. They are usually dirty gray, dark brown or dirty yellow. Blackheads may appear on their surface.
It is most commonly found on the soles of the feet. But they can meet as a group and grow together. Vegetative papillomas grow not only on the outside of the skin, but also deeper.
From the outside, this type of wart may look like normal bones. They are usually semi-circular in shape. However, if the appearance of such skin in a person is constantly evolving, it can become flat.
The appearance of papillomas on the soles of the feet has little to do with age, they can occur in both young and old people. These formations can also be observed in children.
Papillomas of the plant cause discomfort and severe pain when walking. When you step on such a growth, you feel as if you are stepping on a small rock. On the surface, warts can sometimes look like thorns. Therefore, people call this type of papilloma the spine.
At rest, these devices can cause itching. Like other types of papillomas, heel warts are caused by the papilloma virus. The virus usually spreads from the environment to the skin of the feet. For example, it is not uncommon to go to a swimming pool without rubber shoes and become infected. Uncomfortable shoes also contribute to skin damage, as they are more common where shoes rub the feet. It can also cause severe sweating and poor foot hygiene.
It is not recommended to touch the papilloma on the sole of the hand, as this can spread the virus to other parts of the skin.
Treatment of plant warts
Sometimes this type of papilloma can go away on its own. This happens in about half of the cases. But sometimes it takes a long time to wait for this moment, and not everyone can do it, especially if the knowledge itself feels overwhelmed. If the growth of the foot is severely painful and does not allow walking, it should be removed. It is also necessary to remove the knowledge of more than 1 cm. Removal operation can be performed only in the doctor's office.
If there is a suspicion that it is a type of papilloma of the foot, the doctor may perform a number of diagnostic procedures. They will be dissected and analyzed by the horn layer, and PCR analysis for the presence of the papilloma virus genome will be performed. An ultrasound scan is performed to determine the shape and size of the device. Warts on the feet require a differential diagnosis from syphilis warts. However, extensive diagnostic procedures are usually not performed because papilloma of the foot is not difficult to diagnose.
Sometimes medications can be used to reduce the growth of the foot. Preparations made with salicylic acid, necrotizing agents, freezing aerosols and special plasters are suitable for removing warts. However, drug removal is not usually a quick procedure. Only with the help of tools available in medical institutions can you quickly get rid of warts on the soles of the feet. These methods can be:
- laser,
- surgical,
- electrocoagulation,
- cryodestruction,
- radio wave.
Different procedures have their advantages and disadvantages. Surgery, for example, is mainly used for large skin growths because it severely damages the skin.
Warts on the genitals
This is a special type of wart. They are most common in the genital area. Their shape is also unique because they resemble papillae (hence their name). However, the warts may be irregular in shape, resembling cauliflower or a rooster. The viruses that cause this type of wart are usually sexually transmitted. Condylomata can also be found in the mucous membranes and rectum. Therefore, such warts are often called anogenital or venereal. Condylomata are found in the armpits and under the breasts in women. Warts range from bone to pink. Sometimes several genital warts can grow together. Condyloma of this type can also grow to a large size. Warts can cause pain during sex and defecation. If injured, they may bleed. Women with genital warts can develop cervical cancer.
Filiform warts
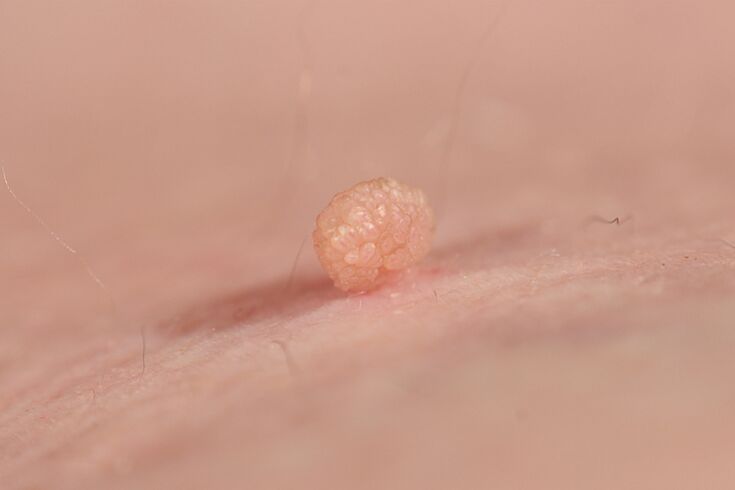
This type of wart is very common. Filiform warts, or acrochords, often grow in large groups. Prefer acrochords for thin skin. This is the area of the armpits, neck, shoulders, eyelids, and nasal wings. May appear in the groin, under the mammary glands of women. They usually do not bother or harm the person, but can cause itching.
Outwardly, fibrous warts look like long threads. However, acrochords with a slender body and a slender spherical or hemispherical stalk are usually found. They are also formal. Such warts are called pentulent.
Most warts of this type range in size from 1 mm to 5 mm. There are also acrochords larger than 1 cm. Sometimes several fibrous warts grow together.
Acrochords are rare in children. They are typical for people over 35 years of age. Their number usually increases with each passing year. This type of wart is 100% found in people over the age of 70. The tendency to have a large number of acrochords in the body can also be inherited. Acrochords are associated with excess weight. In women, they can occur during pregnancy.
Filamentous warts have an unpleasant feature. If the fibrous wart is torn off, a new one will soon appear in its place. Chords are rarely performed on their own. Sweating contributes to their formation, decreased immunity.
Senile warts
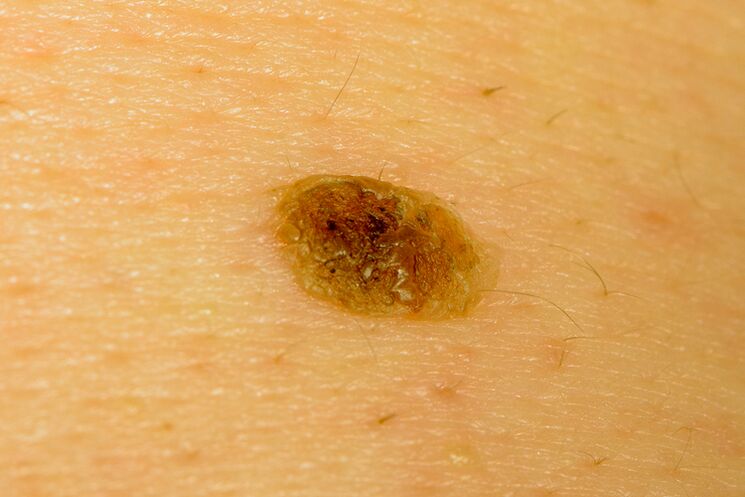
This type of wart has another name - seborrheic keratoma. This usually happens to people over 60 years of age. Unlike other types of warts, senile keratomas are not caused by human papillomavirus. The exact causes of their occurrence have not been determined. Keratomas may be due to age-related changes in the body. They develop from the basal layer of the epidermis, so they are often called basal cell papillomas. In fact, this is a misnomer, because real papillomas are caused only by viruses. Heredity plays a major role in the formation of these neoplasms. Senile keratomas can often resemble melanoma. Therefore, if they appear, you should consult a doctor to determine his diagnosis. However, aging keratomas usually do not require treatment and do not turn into malignant tumors.
Externally, keratomas resemble pink or yellow papules 1-2 mm thick. Their size is from 2 mm to 3 cm. In some cases, the size of such warts reaches 4-6 cm. The keratoma has an oily, easily removable membrane. Their faces are not as smooth as wavy. As they grow, keratomas often resemble mushroom caps and change color to black or dark brown. Their faces may be hard and cracked.
The most common keratomas are in the neck and chest. Can be observed in groups. They appear less on the surface with their hands. They are absent in mucous membranes. Usually, there are no more than 20 keratomas in the body, and if a person has a lot of senile warts, it is usually due to hereditary factors.
Senile keratomas do not go away on their own. People with excess seborrheic keratoma in the body are advised to increase the amount of vitamin C in the diet to prevent new growths. Also, avoid direct sunlight, heat, hypothermia, and stress.
To treat
Most papillomas do not pose a serious risk. However, after an injury, they may bleed and be injured. Then there is the risk of malignant tumors. In papillomas and keratomas, the risk of malignant transformation is much lower than in moles.
Papillomas are usually treated by removal (surgically, cold, high-frequency electricity or laser). Therapeutic effects are usually less effective.
Indications for exclusion are pain in the formation of the skin, its size, bleeding, deformity, inconvenient location (for example, on the toes, soles, genitals), aesthetic considerations. Warts are also removed.














































































